Elimination
of Workplace Hazards
All we need to mitigate the hazards in the workplace
for the safe execution of the task, that results the safe return to our loved
ones. Hierarchy of controls is playing a important role when we think of
mitigation of hazards. The safe control measures what we are taking fall into
the various levels on the hierarchy of controls. The hierarchy of controls
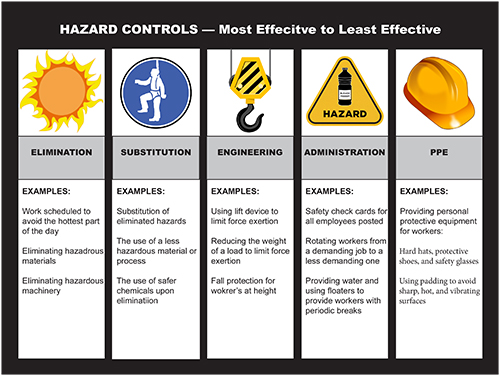
outlines the safe control measures used to mitigate a hazard from most
effective to least effective
SAFETY CULTURE ASSESSMENT CHECK POINTS
A effective version of the hierarchy of control from most effective to least effective control is
Elimination should always be considered on top priority when taking safe controls to mitigate hazards in the workplace.
When employees are not trained to eliminate the hazards or not taking effective engineering controls to protect themselves against hazards, many of them will settle for some type of Personal Protective Equipment’s to attempt to mitigate the chance they are injured.
This will not give the effective safe controls to prevent injuries and accidents in the workplace. safe control measures that comes under the Personal Protective Equipment’s level of the hierarchy of controls are far less effective than safe control measures that eliminate the hazards.
Personal Protective Equipment’s should always be
considered the last line of defense and employees should have this mindset as
well.
HAZARD HIERARCHY
Hazard Elimination
Elimination of hazards is the most effective way to protect employees against injuries in the workplace. However, most of the companies or individual employees do not take the time to plan out work tasks or the time to actually eliminate the hazards they are faced with in the workplace.
Effective job planning, thinking about other safer
ways to complete a job, and allocating the required resources with adequate
quantity to complete the job are some of the first steps supervisors can take
to begin to eliminate the hazards. At shopfloor employees level, identification
of hazard and the elimination mindset is very important to ensure any
additional hazards are eliminated.
Below are the some simple examples of hazard elimination…
Rounding the sharp edge of equipment and facilities to prevent workers injury by the sharp edge hazard.
Installing a CCTV for monitoring the roof conditions of height tower to prevent falling hazards.
Using non-combustible or non-flammable material
instead of combustible or flammable material.
THE NATIONAL FIRE PROTECTION ASSOCIATION(NFPA)






No comments:
Post a Comment